Defibrillator Machine
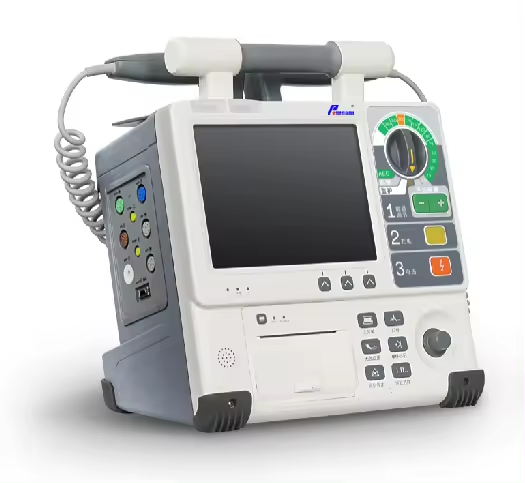
A defibrillator machine is a medical device used to deliver a controlled electrical shock to the heart to restore a normal rhythm in cases of life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias, particularly ventricular fibrillation (VF) and pulseless ventricular tachycardia (VT). Defibrillators are critical in emergency situations, such as cardiac arrest, where immediate intervention can save lives.
Description
Defibrillator Machine
A defibrillator machine is a medical device used to deliver a controlled electrical shock to the heart to restore a normal rhythm in cases of life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias, particularly ventricular fibrillation (VF) and pulseless ventricular tachycardia (VT). Defibrillators are critical in emergency situations, such as cardiac arrest, where immediate intervention can save lives.
Key Features and Functions:
- Electrical Shock Delivery: The primary function of a defibrillator is to deliver a high-energy shock to the heart, which can stop abnormal electrical activity and allow the heart to reestablish an effective rhythm.
- Types of Defibrillators:
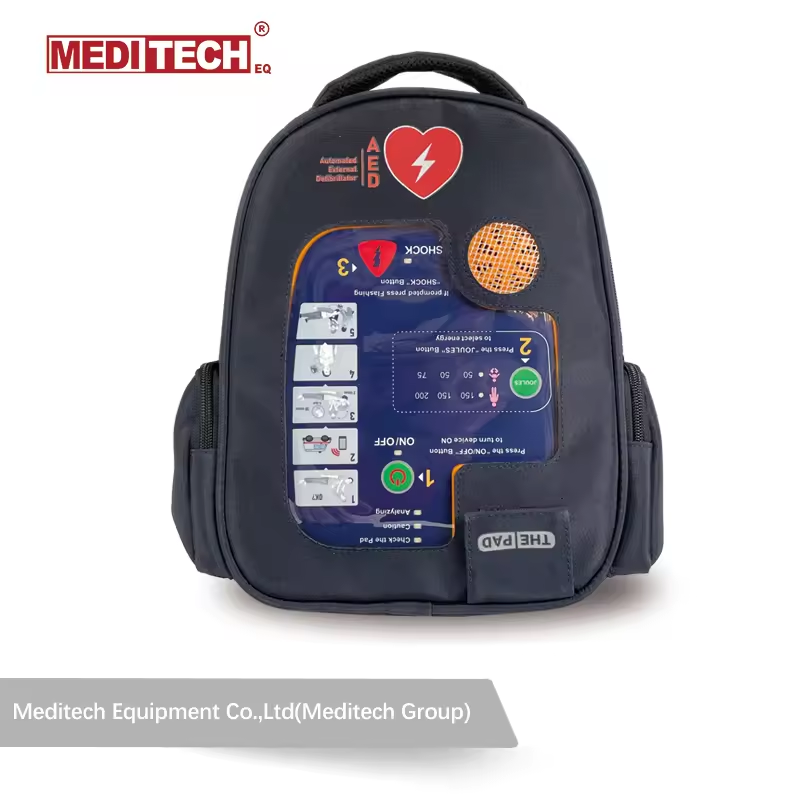
- Automated External Defibrillators (AEDs): Designed for use by laypersons with minimal training. They automatically analyze the heart’s rhythm and provide voice prompts to guide the user through the process.
- Manual External Defibrillators: Used by healthcare professionals. They require the user to interpret the heart’s rhythm and manually set the shock’s intensity.
- Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators (ICDs): Surgically implanted devices that continuously monitor the heart and automatically deliver shocks if an abnormal rhythm is detected.
- Wearable Cardioverter Defibrillators (WCDs): External wearable devices that monitor the heart and deliver shocks as needed, typically used for patients at high risk of sudden cardiac arrest.
- Heart Rhythm Analysis: Defibrillators can analyze the heart’s rhythm to determine if a shock is necessary, minimizing the risk of delivering unnecessary shocks.
- Voice and Visual Prompts: AEDs provide clear instructions and prompts, making them accessible for use by untrained individuals in emergency situations.
- Portability: AEDs are portable and can be found in public places such as airports, schools, and sports arenas, making them accessible during emergencies.
- Data Recording: Some defibrillators record data during use, which can be reviewed by healthcare providers to assess the incident and the device’s performance.
Benefits:
- Life-Saving: Immediate defibrillation can significantly increase the chances of survival and recovery in cardiac arrest situations.
- User-Friendly: AEDs are designed to be used by anyone, with minimal training required, making them effective tools for public health and safety.
- Preventive: ICDs and WCDs provide continuous monitoring and can prevent sudden cardiac death in high-risk patients.
Usage:
- Emergency Response: AEDs are used by first responders, including paramedics, firefighters, police officers, and bystanders, to provide immediate care in cases of sudden cardiac arrest.
- Hospital Settings: Manual defibrillators are used by medical professionals in hospitals and clinics for patients experiencing cardiac emergencies.
Home and Community Settings: ICDs and WCDs are used for ongoing monitoring and protection of patients with known heart conditions at risk of sudden cardiac arrest.








































Reviews
There are no reviews yet.