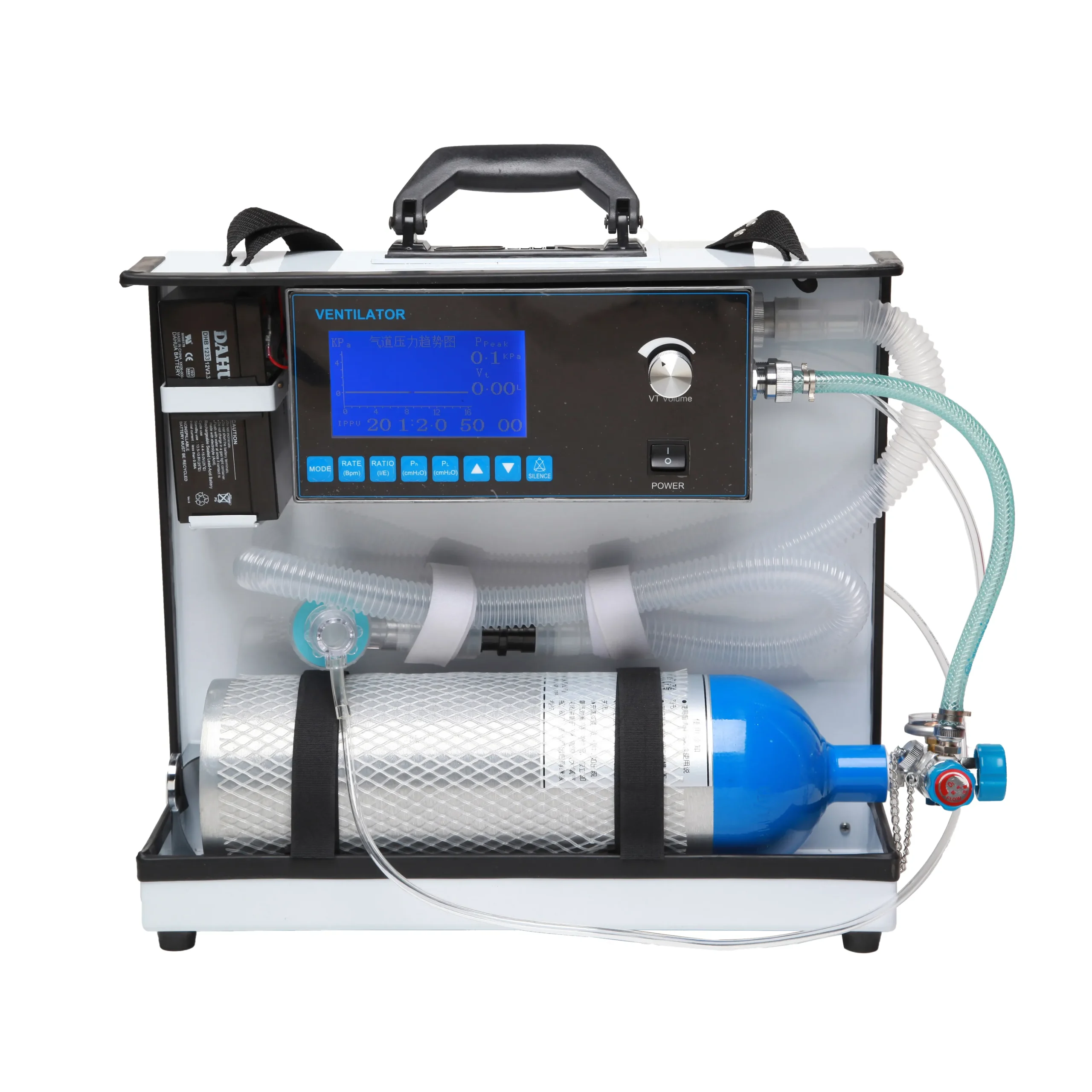
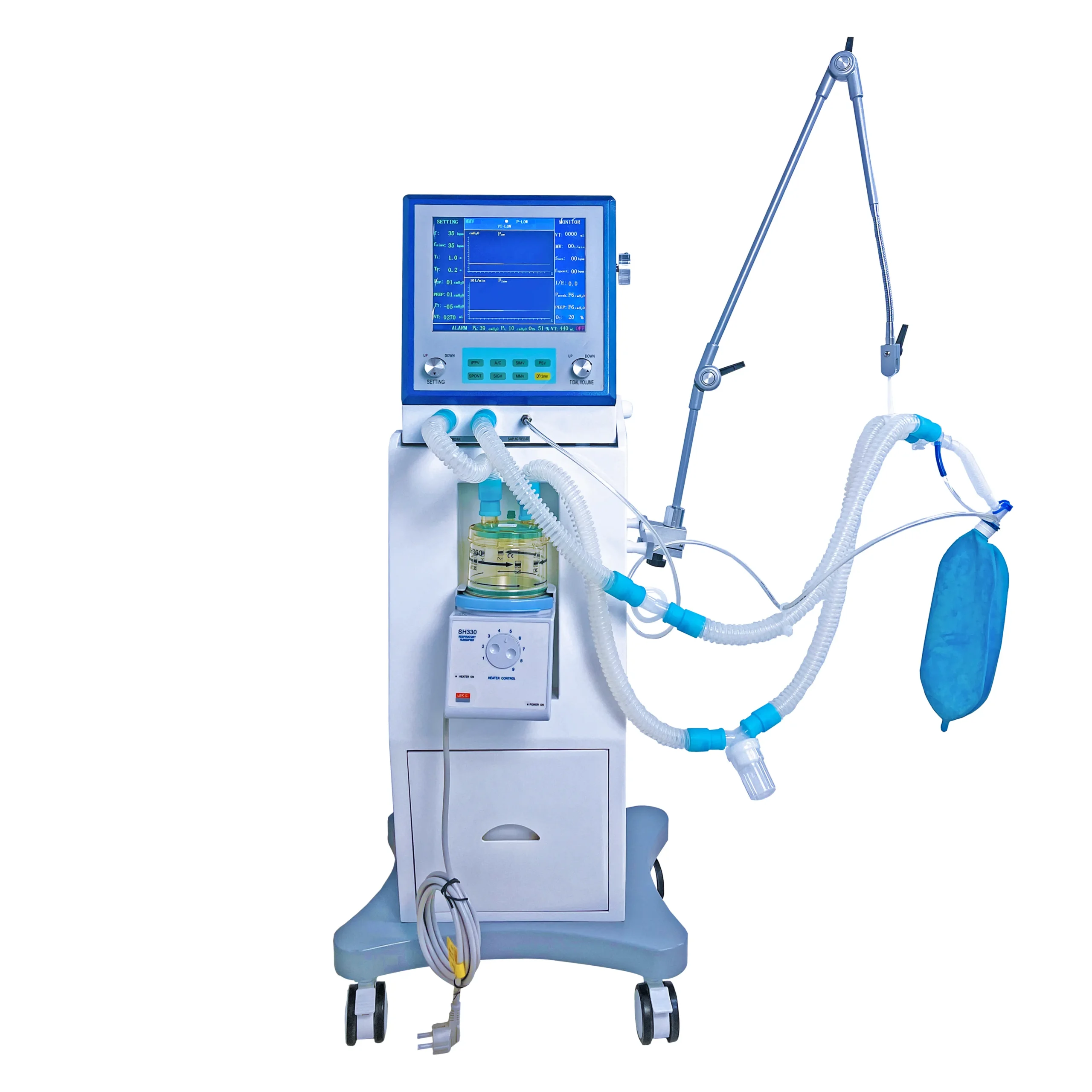
Portable Ventilator
A portable ventilator is a medical device designed to provide mechanical ventilation to patients who have difficulty breathing or are unable to breathe on their own. These devices are compact and lightweight compared to traditional ventilators used in hospitals, making them easier to transport and operate in various settings.
Importance and Impact
Portable ventilators play a crucial role in modern healthcare by extending the reach of critical care beyond hospital walls. They allow for early intervention in emergencies, facilitate safe patient transport, and support long-term respiratory management in community settings. Advances in technology continue to improve their functionality, making them indispensable tools in emergency response, disaster relief efforts, and everyday patient care.
Description
Portable Ventilator
A portable ventilator is a medical device designed to provide mechanical ventilation to patients who have difficulty breathing or are unable to breathe on their own. These devices are compact and lightweight compared to traditional ventilators used in hospitals, making them easier to transport and operate in various settings.
Key features of portable ventilators typically include:
- Mechanical Support: They deliver controlled amounts of oxygen and air to the lungs, assisting or replacing spontaneous breathing.
- Mobility: They are designed to be easily transported and operated outside of hospital settings, such as in ambulances, home care environments, or during transport between facilities.
- Battery Powered: Many portable ventilators are equipped with rechargeable batteries, allowing them to function without being plugged into an external power source for a period of time.
- Settings and Alarms: They offer adjustable settings for parameters such as respiratory rate, tidal volume (amount of air per breath), and oxygen concentration. They also include alarms to alert caregivers to changes in patient condition or equipment malfunctions.
- Monitoring Capabilities: Some models include monitoring features to assess the patient’s respiratory status and the effectiveness of ventilation.
Portable ventilators are crucial in providing respiratory support in emergency situations, during patient transport, or in remote locations where access to standard medical equipment may be limited. Their development has significantly enhanced the ability to provide critical care in diverse environments outside of traditional hospital settings.
Components and Functionality
- Ventilation Modes:
- Portable ventilators typically offer a range of ventilation modes suited to different patient needs, such as:
- Volume Control Ventilation (VCV): Delivers a set tidal volume with each breath.
- Pressure Control Ventilation (PCV): Maintains a set airway pressure during inspiration.
- Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP): Provides a continuous positive pressure to keep the airways open, often used in non-invasive ventilation.
- Bi-level Positive Airway Pressure (BiPAP): Offers two levels of pressure, higher during inspiration and lower during expiration, useful for patients with conditions like sleep apnea or respiratory failure.
- Portable ventilators typically offer a range of ventilation modes suited to different patient needs, such as:
- Size and Portability:
- Portable ventilators are compact and lightweight, designed for easy transportation and use in various settings. They are typically smaller than traditional hospital ventilators, making them suitable for ambulances, aircraft, home care, and field hospitals.
- Power Source:
- Many portable ventilators are battery-powered, with rechargeable batteries that provide several hours of operation. This feature is critical during transport or in situations where continuous power supply may be unavailable.
- User Interface:
- The interface of portable ventilators is designed to be user-friendly, allowing healthcare providers to adjust settings such as respiratory rate, tidal volume, FiO2 (fraction of inspired oxygen), and alarms easily. Clear displays provide real-time feedback on patient parameters and ventilator status.
- Monitoring and Alarms:
- Portable ventilators include built-in monitoring capabilities to assess parameters like tidal volume, respiratory rate, and oxygen saturation (SpO2). They also feature alarms that notify caregivers of issues such as high or low tidal volumes, apnea, disconnection, or low battery.
- Durability and Reliability:
- Given their intended use in diverse environments, portable ventilators are built to withstand rugged conditions and maintain reliability. They undergo testing to ensure they can operate effectively during transport and in varying climates.
- Application:
- Portable ventilators are used in a range of clinical scenarios, including:
- Emergency Medical Services (EMS): For ventilating patients during transport to hospitals.
- Home Care: Enabling patients with chronic respiratory conditions to receive ventilatory support at home.
- Military and Disaster Response: Providing critical care in field hospitals and remote locations where infrastructure is limited.
- Portable ventilators are used in a range of clinical scenarios, including:
Importance and Impact
Portable ventilators play a crucial role in modern healthcare by extending the reach of critical care beyond hospital walls. They allow for early intervention in emergencies, facilitate safe patient transport, and support long-term respiratory management in community settings. Advances in technology continue to improve their functionality, making them indispensable tools in emergency response, disaster relief efforts, and everyday patient care.


































Reviews
There are no reviews yet.