Stethoscope
Stethoscope
A stethoscope is a medical instrument used by healthcare professionals to listen to the internal sounds of a patient’s body, typically the heart, lungs, and intestines. It is an essential tool in the practice of medicine, aiding in the diagnosis and monitoring of various health conditions.
Description
Stethoscope
A stethoscope is a medical instrument used by healthcare professionals to listen to the internal sounds of a patient’s body, typically the heart, lungs, and intestines. It is an essential tool in the practice of medicine, aiding in the diagnosis and monitoring of various health conditions. Here are the key features and details about a stethoscope:
Components of a Stethoscope
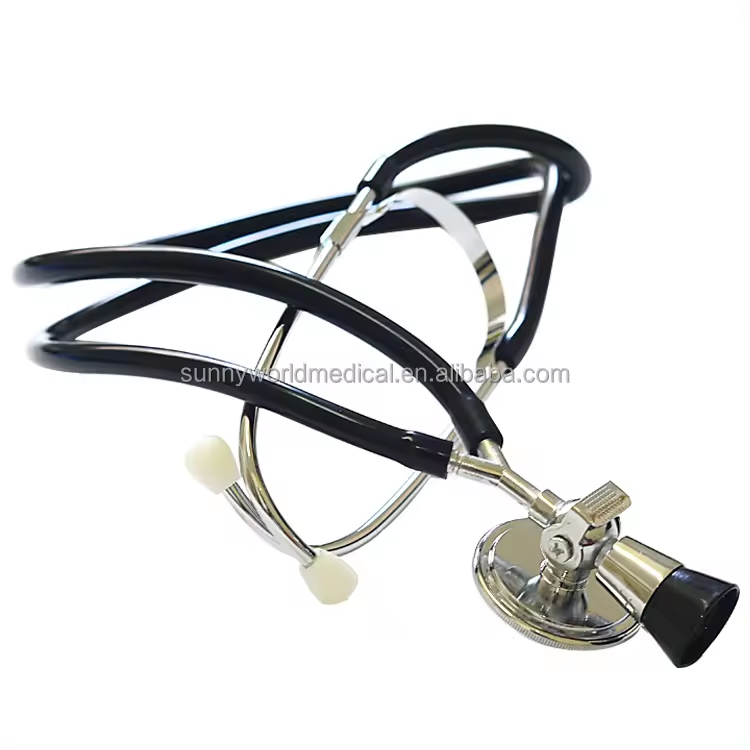
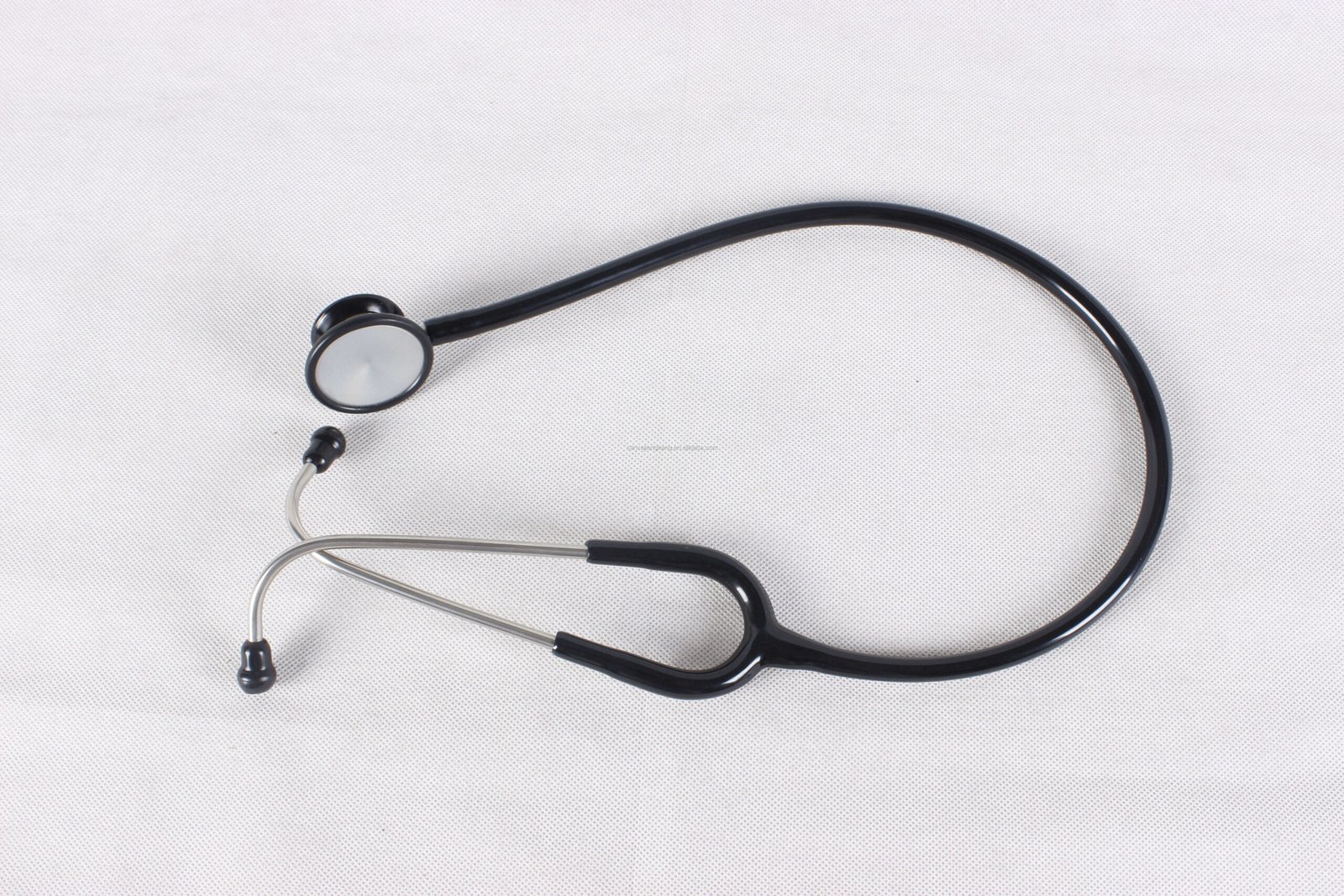
- Chest Piece
- Diaphragm: A flat, round part of the chest piece used to hear high-frequency sounds, such as normal heartbeats and breath sounds.
- Bell: A smaller, cup-shaped part used to detect low-frequency sounds, such as heart murmurs and some bowel sounds. Not all stethoscopes have a bell; some have a dual-diaphragm design instead.
- Tubing
- Acoustic Tubing: Flexible tubing that transmits sound from the chest piece to the earpieces. High-quality stethoscopes use thicker tubing to reduce noise interference and enhance sound clarity.
- Binaural Tubing: The part of the tubing that splits into two and connects to the earpieces. It is often adjustable to ensure a comfortable fit.
- Earpieces
- Ear Tips: Soft, silicone or rubber tips that fit snugly into the user’s ears, creating a seal to block out external noise.
- Binaurals: The metal tubes that connect the earpieces to the acoustic tubing. They are typically adjustable for a comfortable and secure fit.
Types of Stethoscopes
- Acoustic Stethoscopes
- The most common type, which relies on sound waves transmitted through the tubing. They can be further categorized into:
- Single-head Stethoscopes: Have only a diaphragm or a bell.
- Dual-head Stethoscopes: Have both a diaphragm and a bell on opposite sides of the chest piece.
- The most common type, which relies on sound waves transmitted through the tubing. They can be further categorized into:
- Electronic Stethoscopes
- Use electronic amplification and filtering to enhance body sounds, making it easier to hear faint or low-frequency sounds. Some models also offer features like digital recording and Bluetooth connectivity for data transfer.
- Fetal Stethoscopes (Fetoscopes)
- Specialized stethoscopes used to listen to the fetal heartbeat during pregnancy. They have a different design, often resembling a trumpet, to amplify the sound of the fetal heartbeat.
Applications of a Stethoscope
- Cardiology
- Used to listen to heart sounds, including heartbeats, murmurs, and other abnormalities.
- Respiratory
- Used to auscultate lung sounds, including breath sounds, wheezes, and crackles, to diagnose conditions like pneumonia, asthma, and other respiratory illnesses.
- Gastrointestinal
- Used to listen to bowel sounds, which can help diagnose intestinal blockages or other gastrointestinal issues.
- Blood Pressure Measurement
- Used in conjunction with a sphygmomanometer to measure blood pressure by listening to the Korotkoff sounds.
Considerations When Choosing a Stethoscope
- Acoustic Quality
- High-quality stethoscopes provide clearer and more precise sound transmission, essential for accurate diagnosis.
- Comfort
- Earpieces and tubing should be comfortable to use, especially for extended periods. Adjustable binaurals and soft ear tips enhance comfort.
- Durability
- Stethoscopes should be made of durable materials to withstand frequent use and cleaning.
- Special Features
- Consider additional features such as electronic amplification, digital recording, and specialized chest pieces for specific applications.
Care and Maintenance
- Cleaning
- Regular cleaning of the chest piece, tubing, and earpieces is essential to prevent the spread of infection.
- Storage
- Store the stethoscope in a clean, dry place. Avoid exposing it to extreme temperatures or direct sunlight, which can damage the tubing and other components.
- Regular Inspection
- Periodically check for wear and tear, such as cracks in the tubing or loose earpieces, and replace parts as necessary to maintain optimal performance.












































Reviews
There are no reviews yet.