Anesthesia Machine
An anesthesia machine is a critical piece of medical equipment used to support and control the delivery of anesthetic gases to patients during surgery and other medical procedures. Its primary functions include delivering a precise and continuous supply of medical gases (such as oxygen and nitrous oxide), anesthetic agents (such as volatile anesthetics), and ensuring proper ventilation of the patient’s lungs.
Anesthesia machines are designed to ensure patient safety, precision in the delivery of anesthetic gases, and adaptability to various clinical situations. Their proper use requires specialized training for anesthesiologists and other medical professionals.
Description
Anesthesia Machine
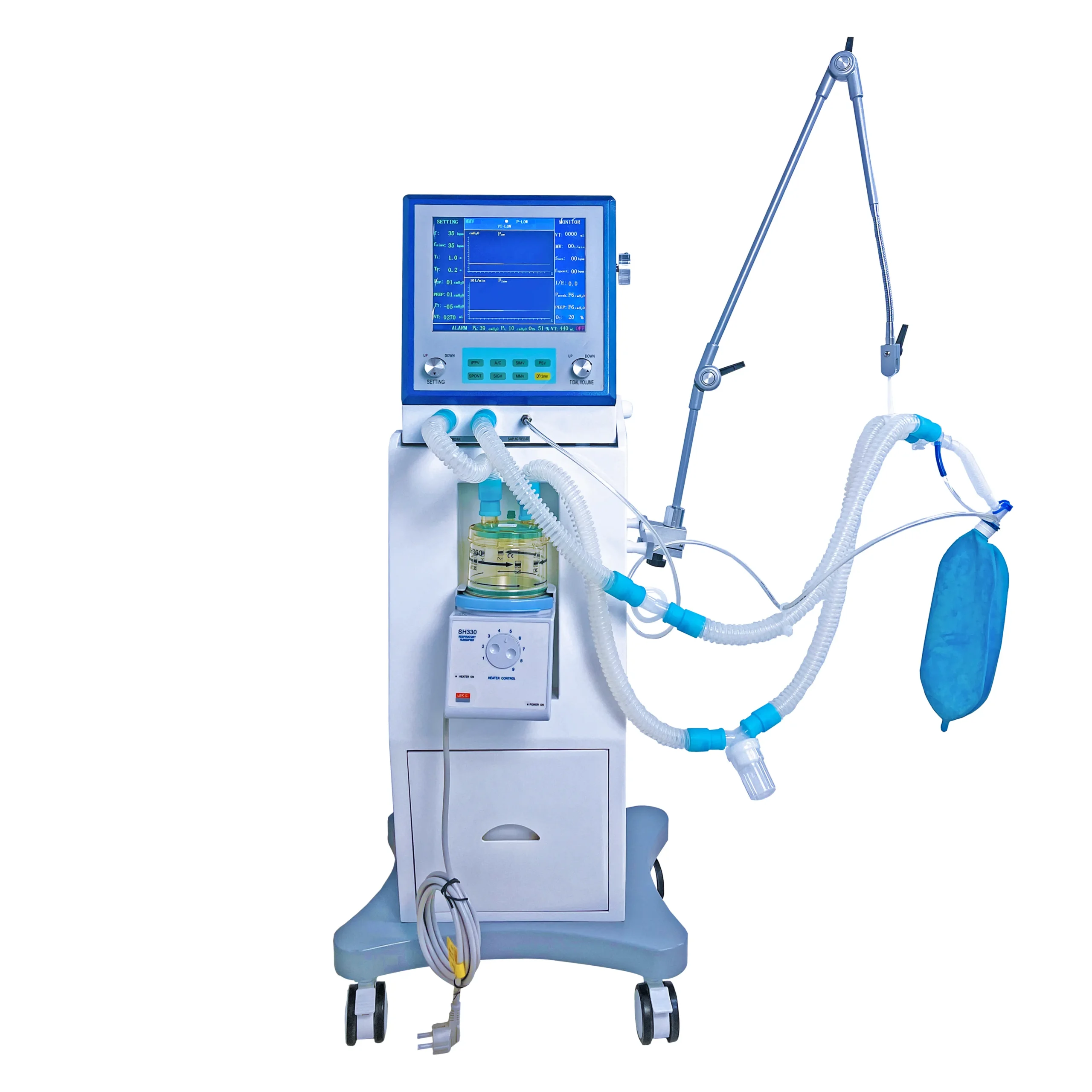
An anesthesia machine is a critical piece of medical equipment used to support and control the delivery of anesthetic gases to patients during surgery and other medical procedures. Its primary functions include delivering a precise and continuous supply of medical gases (such as oxygen and nitrous oxide), anesthetic agents (such as volatile anesthetics), and ensuring proper ventilation of the patient’s lungs. The main components and functions of an anesthesia machine include:
- Gas Supply:
- Oxygen and Nitrous Oxide: Anesthesia machines are connected to hospital gas pipelines or gas cylinders that supply oxygen, nitrous oxide, and sometimes medical air.
- Flowmeters: These regulate and measure the flow of each gas delivered to the patient.
- Vaporizers:
- These devices convert liquid anesthetic agents into vapors that can be mixed with the carrier gas (oxygen or a mixture of oxygen and nitrous oxide) and delivered to the patient.
- Breathing Circuit:
- Patient Circuit: This is a system of tubes and valves that delivers the anesthetic gases to the patient and removes exhaled gases.
- Carbon Dioxide Absorber: This component removes carbon dioxide from the exhaled gases so that they can be safely recirculated.
- Ventilation System:
- Manual Ventilation (Bag): Allows the anesthesiologist to manually control the patient’s breathing.
- Mechanical Ventilator: Provides controlled, automatic ventilation, especially useful during longer surgeries or when precise control of breathing is required.
- Monitors and Alarms:
- Gas Concentration Monitors: These monitor the concentration of oxygen, nitrous oxide, and anesthetic gases.
- Patient Monitors: These include devices to monitor vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation.
- Alarms: These alert the anesthesiologist to any issues such as low oxygen supply, high or low pressure in the breathing circuit, or other potential problems.
- Scavenging System:
- This system captures and removes excess anesthetic gases from the operating room to protect healthcare personnel from exposure.
Anesthesia machines are designed to ensure patient safety, precision in the delivery of anesthetic gases, and adaptability to various clinical situations. Their proper use requires specialized training for anesthesiologists and other medical professionals.













































Reviews
There are no reviews yet.