Glucometer
Glucometer
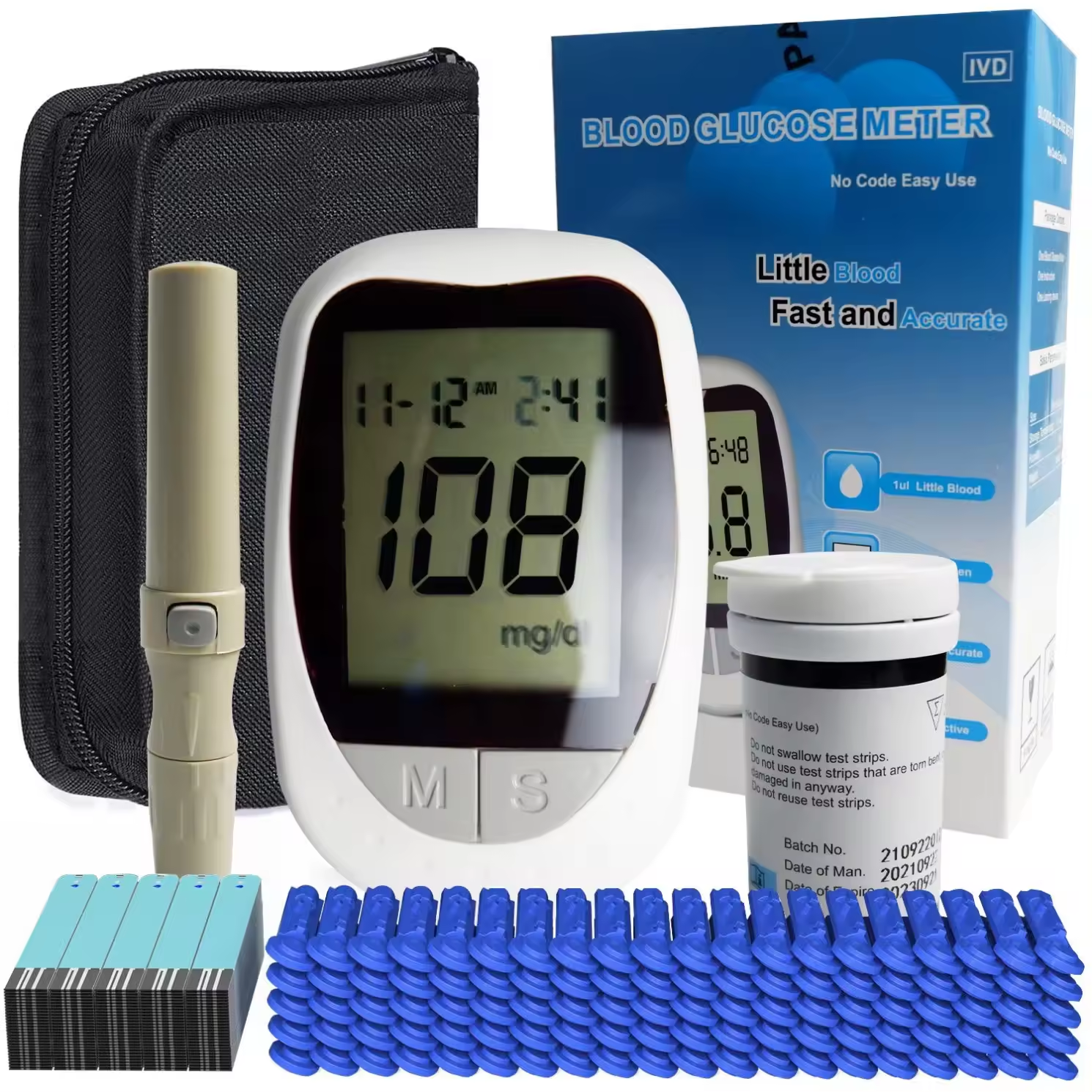
A glucometer, also known as a glucose meter, is a medical device used to measure the approximate concentration of glucose in the blood. It is an essential tool for people with diabetes to monitor their blood sugar levels and manage their condition effectively.
Description
Glucometer
A glucometer, also known as a glucose meter, is a medical device used to measure the approximate concentration of glucose in the blood. It is an essential tool for people with diabetes to monitor their blood sugar levels and manage their condition effectively. Here is a detailed overview of a glucometer:
Components of a Glucometer
- Meter Device
- Display Screen: Shows the blood glucose level reading, and may display additional information such as date, time, and stored readings.
- Buttons: Used to navigate the device’s menu, set the date and time, and review past readings.
- Test Strips
- Small, disposable strips that contain chemicals which react with glucose in the blood. Each strip is inserted into the glucometer to perform a test.
- Lancing Device
- A small, pen-like instrument that holds a lancet (a small, sharp needle). It is used to prick the skin to obtain a drop of blood.
- Lancets
- Small needles used with the lancing device to draw a drop of blood. They are typically single-use to maintain hygiene and prevent infection.
How a Glucometer Works
- Preparation
- Wash and dry hands thoroughly to ensure accuracy and prevent contamination.
- Inserting the Test Strip
- Insert a new test strip into the glucometer. The device usually powers on automatically once the strip is inserted.
- Obtaining a Blood Sample
- Use the lancing device to prick the side of a fingertip to obtain a drop of blood.
- Applying the Blood
- Touch the edge of the test strip to the blood drop. The strip will draw in the blood by capillary action.
- Reading the Result
- The glucometer will analyze the blood sample and display the blood glucose level on the screen within a few seconds.
Features of Modern Glucometers
- Memory Storage
- Stores a certain number of past readings, allowing users to track their glucose levels over time.
- Data Transfer
- Some glucometers can connect to computers, smartphones, or other devices via USB, Bluetooth, or wireless technology to transfer data for further analysis.
- Automatic Coding
- Modern glucometers often come with automatic coding, eliminating the need to manually input a code for each new batch of test strips.
- Alternative Site Testing
- Some devices allow for blood samples to be taken from alternative sites, such as the palm or forearm, which can be less painful than fingertip testing.
- Ketone Testing
- Some advanced models also offer the ability to test for ketones in the blood, which is important for managing diabetic ketoacidosis.
Importance of Glucometers
- Diabetes Management
- Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels helps individuals with diabetes make informed decisions about diet, exercise, and medication.
- Prevention of Complications
- Maintaining optimal blood glucose levels helps prevent complications associated with diabetes, such as neuropathy, retinopathy, and cardiovascular disease.
- Personalized Care
- Enables healthcare providers to tailor treatment plans based on accurate and timely blood glucose readings.
Tips for Accurate Readings
- Proper Storage
- Store test strips in a cool, dry place and use them before their expiration date.
- Calibration
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for calibrating the glucometer if required.
- Clean Hands
- Always test with clean, dry hands to avoid contaminating the blood sample.
- Consistent Testing Time
- Test at the same times each day, such as before meals and at bedtime, to track glucose trends accurately.
Care and Maintenance
- Regular Cleaning
- Clean the glucometer and lancing device regularly as per the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Battery Replacement
- Replace the batteries when needed to ensure the device functions properly.
- Quality Control Tests
Use control solutions periodically to check the accuracy of the glucometer.









































Reviews
There are no reviews yet.