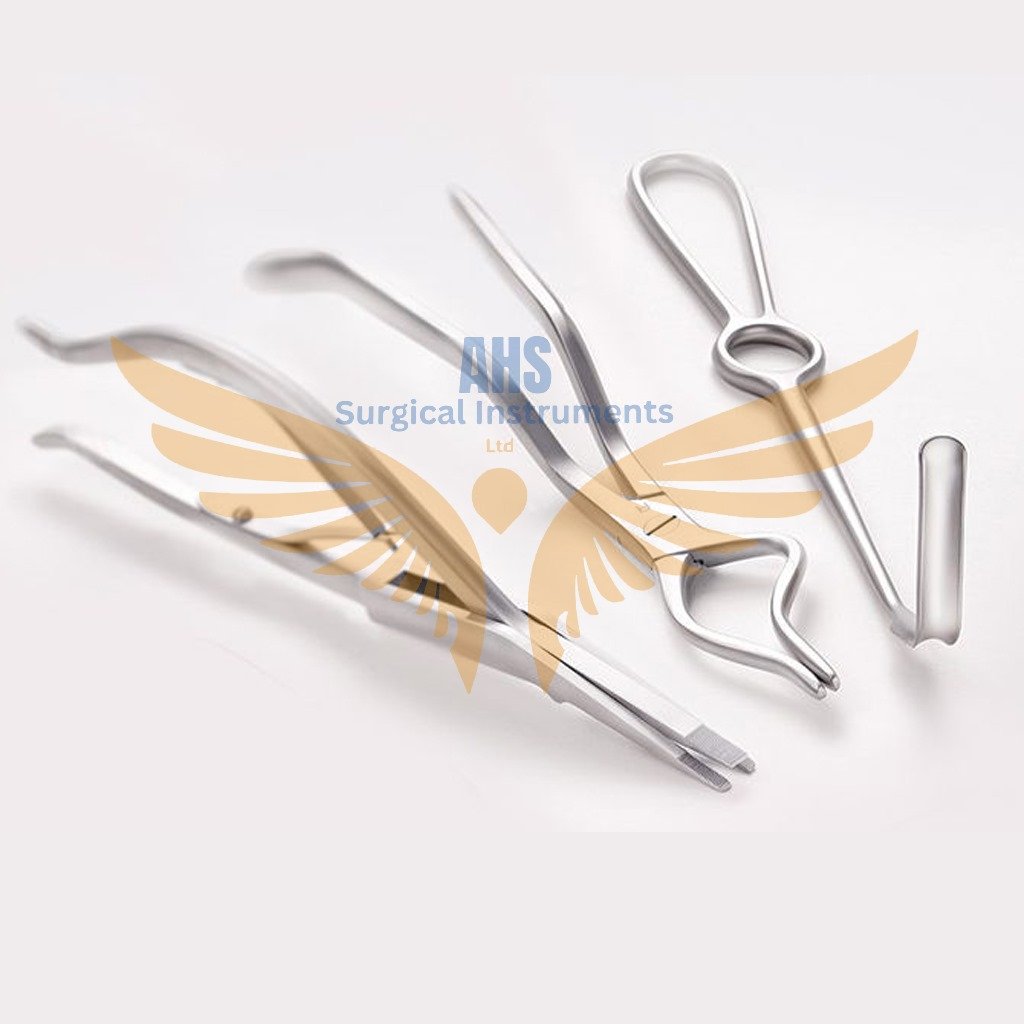
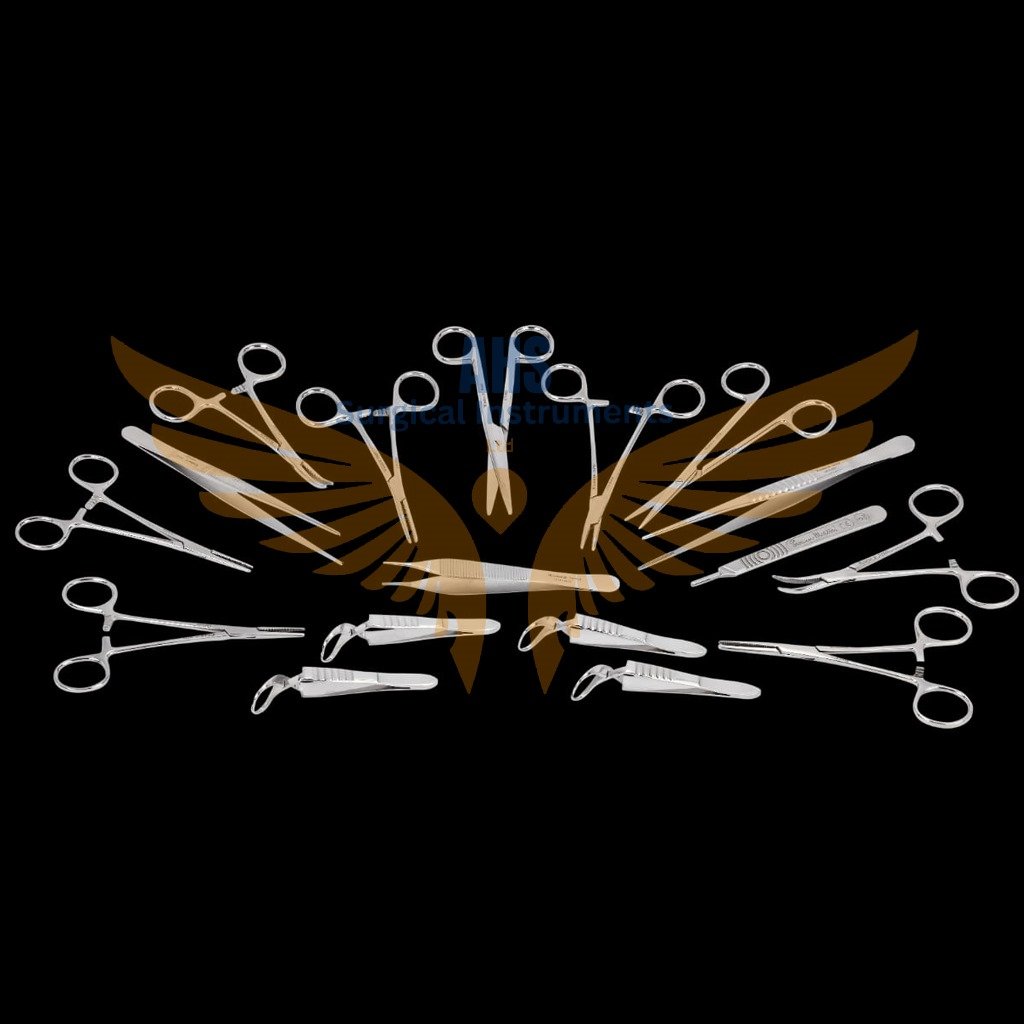
General Surgical Instruments
0,00 د.إ
General surgical instruments encompass a wide range of tools used in various surgical procedures. Here’s a brief overview of some common types:
- Scalpel: A small, sharp knife used for making incisions.
- Forceps: Tweezer-like instruments used for grasping tissues or objects.
- Scissors: Cutting instruments used for cutting tissues or sutures.
- Needle Holder: Used to hold and manipulate surgical needles and sutures.
- Retractor: Used to hold back tissues or organs to provide access to the surgical site.
- Surgical Suction: Used for removing fluids or debris from the surgical area.
- Hemostats: Used for clamping blood vessels or tissue to control bleeding.
- Surgical Sutures: Used to close wounds or incisions after surgery.
- Trocar and Cannula: Used for creating access ports in minimally invasive surgery.
- Speculum: Used to enlarge the opening of a canal or cavity for examination.
These instruments are crucial for performing a wide range of surgical procedures with precision and safety.
Description
-
- Sale! Add to cart
- Amalgam, Dental Restorative Materials
Angie Defense Chroma Kit
- Original price was: 195,00 د.إ.178,00 د.إCurrent price is: 178,00 د.إ.
-
- Sale! Add to cart
- Medical Clothing, Medical Consumables
Disposable Isolation Gown
- Original price was: 23,00 د.إ.19,00 د.إCurrent price is: 19,00 د.إ.
-
- Sale! Add to cart
- Cements, Dental Restorative Materials
ZINC OXIDE Fast (Powder for Making Dental Fillings in Paste)
- Original price was: 75,00 د.إ.55,00 د.إCurrent price is: 55,00 د.إ.
-
- Sale! Add to cart
- Medical Consumables, Syringes and needles
ENDO TOP (Endo Irrigation Needles)
- Original price was: 215,00 د.إ.207,00 د.إCurrent price is: 207,00 د.إ.
-
- Sale! Add to cart
- Dental Anesthetic Supplies, Local anesthetics
BLUE ETCH 50 ml (Dental Etching Gel)
- Original price was: 195,00 د.إ.179,00 د.إCurrent price is: 179,00 د.إ.
-
- Sale! Add to cart
- Dental Anesthetic Supplies, Local anesthetics
ZirClean , cleaning agent
- Original price was: 105,00 د.إ.103,00 د.إCurrent price is: 103,00 د.إ.































Reviews
There are no reviews yet.